Each eCommerce store has two goals ahead of it – to drive more money and have a decent profit margin. Without these two factors, the entire business model might be considered a waste. Any dropshipping business is aware that maintaining low-profit margins for a significant period might result in a severe financial loss and cease operations.
This article will review profit margin, the excellent profit margins in dropshipping, and how to correctly calculate any costs related to your business to see the bigger picture.
What is Dropshipping Profit Margin?
We can not be talking about net income, profits, expenses, and all that without defining profit margin. It is the amount of money you are left with after deducting the costs from the revenue.
Example
You sell a pair of boots on your eCommerce website for a selling price of $100. Your total expenses are $90, and your net earnings are $10.
Of course, this is an actual example of how dropshipping businesses are making their profits. There are many details to fix to formulate the final price, including finding a niche market, wholesale price, ad spend, and others.
What is a Good Profit Margin in Dropshipping?
While a low profit margin is one that usually is below 5-10%, defining a good one might be a challenging task. First of all, we need to say that the average margin doesn’t matter unless we sell in volumes. If seller A trades $100,000 per month with a 10% profit margin (which is considered bad), it is still better than seller B, which has $5,000 in sales, with a 25% profit margin.
In most cases, average drop shipping profit margins will be between 15%-20%, depending on the product being sold and where it’s being sold. It will also be in your best interest to try to go for a profit margin of around 20% — dropshippers can accomplish this by focusing on products with high demand and a low supply, as well as avoiding extra fees from sellers.
One old dropshipping strategy states that 33% of your product price should be product cost, another one-third you should dedicate to ads, and the last third should be your profit. While this might work sometimes, it is generally not good to keep things that simple. A, usually, they are not.
Operating on slim margins is a tough game.
Get the most out of your data and increase your profits.
How to Calculate Profit Margins for your Dropshipping Store?
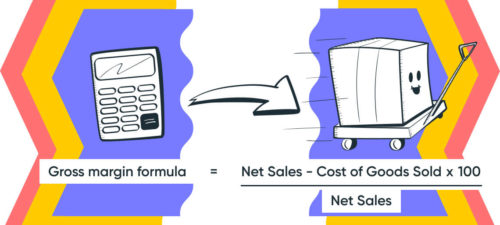
The profit margin is calculated with a simple formula.
Net profit margins = [(Revenue – Cost) / Revenue] * 100.
While calculating your revenue might not be that hard to calculate (amount of orders * sales price), costs are a bit harder to predict, as there are many things to consider before drawing the line.
How to Define Your Products’ Price?
Calculating e-commerce profits can feel complicated, but it doesn’t have to be. You should have access to everything you need to calculate your returns and profits at your fingertips, which means having the wholesale price for all of your items. Having a firm understanding of how the costs on your site translate into the price that a customer sees is essential to running a successful online store.
But sellers often prefer to set high profit margins, as it seems logical – you lift the price, you reap the benefits of it. We said it previously, and we will repeat it – the devil is in the detail. If your fees are much steeper than those offered by your competitors, you need to show some severe arguments to create a market demand for your products and increase your customer base.
So, which are the most significant factors that decide your pricing model for the products in your catalog?
1. Shipping fees
What is the point of delivering a product to its final destination if the customer can’t use it? That’s where shipping comes in. It’s one additional part of your business that doesn’t necessarily have to bring in revenue directly. Still, it has to be compelling enough so that your customers don’t feel like they’re being taken advantage of.
It is a standard practice for all products to “absorb” the delivery charge. So, if your goods cost $20,00 but you charge $10,00 for shipping, aim for a selling price of $30 with FREE shipping.
2. Returns/chargebacks
Product returns are a pain. You cannot predict if a client will return their goods. You can also get scammed by customers who create false chargebacks to receive free goods. Others are returning their products in awful condition, meaning you can no longer list them as new. This creates a massive problem for sellers. If any online business wants to succeed, they should consider chargebacks and returns as one good way to protect themselves from fraudulent activities.
3. Advertising costs
Dropshipping is a bit different than other industries. One of the most significant differences is that one of the biggest reasons stores fail or succeed is staying afloat with their ad costs. Finding new customers is almost impossible without substantial marketing expenses since everyone is selling more or less the same product. Making more sales relies heavily on how you manage Facebook and Google ads.
4. Product sourcing
Finding profitable products is pivotal in running a successful dropshipping store. You need to consistently find trending products (Google trends is a perfect indicator) and always sell fast-moving stock to ensure you won’t experience long periods without sales.
5. Product cost
Last but not least comes the product cost. After all, it is the highest cost to eCommerce stores, and it lays the foundation of everything and establishes the business model. If the buying price is too huge, you can expect different profit margins than competitors who hold your product for a much lower cost, thus saving a couple of percent off the unit price.

Do You Need to Pay Any Fees or Commissions in Dropshipping?
This is where it gets interesting. You may need a website with shopping cart functionalities to sell well. Of course, you can sell on eBay, Amazon, etc., but we need to warn you that drop shipping goods sold on the marketplaces are often flagged, leading to account suspension and money loss.
Of course, just because it is more problematic doesn’t mean you shouldn’t consider shutting down the option to sell on Amazon, eBay, Etsy, and other marketplaces.
Marketplaces – commission fees, plans, and conditions
Before we mention how much platforms charge, we need to say something. Arbitrage selling is not accepted on most marketplaces, meaning you will be banned if you get caught. With immediate notice. To avoid sanctions, you have to fulfill several conditions:
Be the seller of the listings – for all products.
Remove any information that might lead to the third-party seller before order shipment.
Accept and process returns from your address.
Have your name included in all packing slips, invoices, and in general – everything associated with your products.
Once you have fulfilled the conditions, it’s time to sell:
Amazon
Amazon is the go-to place for many drop shippers. Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) means you will find sending goods to their logistics centers very convenient. You have to pay for storage fees (if you use Amazon’s delivery services) and referral fees, which might reach well over 20% for more expensive products while they usually are claimed to vary between 8-15%.
Amazon charges $39.99 per month, but otherwise, you have to pay $1 each time an item of yours sells. It is quite a lot, especially if you’re selling higher volume items with low profit margins.
eBay
eBay charges a selling fee of up to 15% of the total amount of each sale (item price, postage, and all fees that come along) plus a processing order fee ($0.30 per order). The problem with eBay is that you should pay while you get some listings for free if you need to list more. You can also pay to get an eBay subscription, but your price only increases with that.
While eBay is a bit cheaper initially, it costs more in the long run than Amazon.
Shopping Carts
For many sellers, Amazon and eBay are way off the mark. Selling on a third-party marketplace can drive traffic, but it comes with many additional fees that might become unbearable for retailers. It is where shopping carts have stepped ahead.
They give you more flexibility and make dropship much more manageable – no restraints at all. Of course, that doesn’t mean you’ll have less competition. However, you would witness some terrific savings.
Shopify
Shopify is a hosted e-commerce platform. It is probably the most notable name in the industry, with over a million sellers worldwide. Customers are well aware of the themes, and there are many conveniences for retailers.
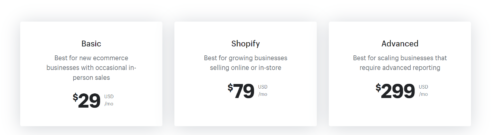
Shopify has four pricing plans: Basic, Shopify, Advanced, and Shopify Plus (which you won’t find in the regular pricing models). The platform charges based on the company size. If you’re a small seller, you need to pay $29 per month, while you may need to pay more for higher plans.
You need to consider app costs and processing fees- if you have apps, you will have to pay extra. But even so, it doesn’t come close to what you might have to spend on big marketplaces.
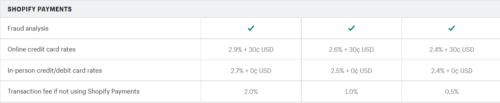
You need to consider app costs and processing fees – if you have apps, you will have to pay extra. But even so, it doesn’t come close to what you might have to spend on big marketplaces.
Magento
Magento is a prevalent name in the industry. It has an open-source solution for SMBs and a paid one for enterprise solutions (Adobe Commerce/Adobe Cloud Commerce). You need to consider that you should have vast technical knowledge, so you will have to splash money to pay a developer to list your items, as it’s the most skill-requiring option available from the ones mentioned earlier.
However, not everything is free. You should pay for the hosting, SSL protocols, as well as payment processing fees. On top of that, you may need to find reliable apps which cost you additional money.
Magento is a fantastic solution for high-caliber dropshippers, but it is not a good option for starters.
How Can You Increase Your Profit Margin in Dropshipping?
You have to fight for every dollar available to increase your profit margins.
1. Upsell
One of the most potent ways to increase your profit margins is upselling or cross-selling your products. You can offer premium add-ons to your existing products to increase the average basket value.
2. Negotiate Prices with Suppliers
A successful seller does not make customers pay a premium for the same product, and it’s the one that can force suppliers to reduce prices, thus increasing the profit margin without increasing the cost. On the one hand, you avoid upsetting customers by lifting prices, and on the other hand – you make more sales.
3. Automate Operations
Automations could be pretty handy. Using software to cover most of the heavy lifting would mean you can save a lot of money from staff. Automating your business processes could help you save time and money.
4. Establish a Brand
One way to distinguish yourself from other businesses is to establish your brand. Having a unique brand might not be a big deal at first sight, but it can give you so much added value in the long run. It is tough to create a brand in dropshipping, but it is not impossible.
Operating on slim margins is a tough game.
Get the most out of your data and increase your profits.
FAQs
Is Dropshipping Profitable in 2022?
Dropshipping will be profitable in 2022. And while there are so much more competitors than a decade ago, you can still make an outstanding amount of money with dropshipping and enjoy good profit margins.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Dropshipping?
Dropshipping is about selling trendy products. Also, you don’t need to invest a whole lot of money, as you have a low overhead cost, and there’s no need to buy inventory upfront. On the other hand, you are heavily reliant on third-party suppliers, which means you could destroy your reputation, and it might not even be your fault for it. Limited control over the quality and stock numbers might also be a problem in the long term.

